Khabarovsk Territory greets travelers with its natural resources. There are several nature reserves, national parks and wildlife sanctuaries on its territory, which show how reverently the locals are about the preservation of heritage. In addition to beauty in a general sense, there are also truly unique phenomena, such as lakes covered with blooming lotuses, or Toki Islands, where pinnipeds are comfortable.
The cities also have a lot of interesting things: from monuments to historical figures to museums with a rich collection of works of art. Orthodox Christians can visit churches and cathedrals built in modern times. And everyone, without exception, will love city parks and recreation areas that will save you from boredom and lift your spirits.
The most famous and beautiful places in the region
List, photos with names and descriptions of attractions worth visiting!
Dusse-Alin
A mountain range with a length of 150 km. The highest point is 2.1 thousand meters. Since most of the territory is remote from civilization, the pristine nature has been preserved here. In 1987, on an area of almost 357 thousand hectares, the Bureinsky Reserve was formed - a reserve, where there is an exemplary area of mountain taiga. In addition to Dusse-Alin, the decoration of these places is the Bear Lake, located on the slopes of the ridge. It is not only mountainous, but also glacial. The reservoir is as if sealed on three sides in a stone bag. The water surface is blue and clear. Tourists can visit the territory only in groups accompanied by the reserve workers.

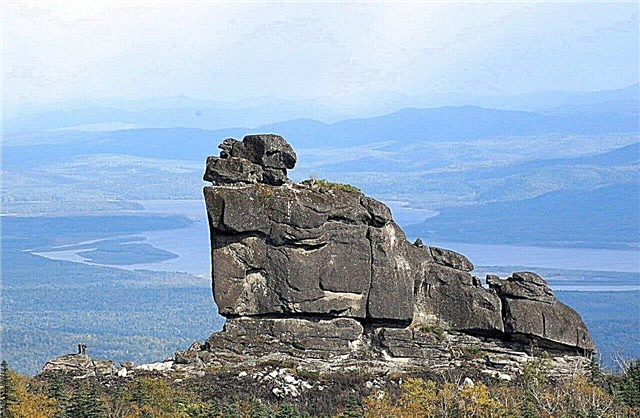
Amur pillars
They belong to the Komsomolsk district. They can be found almost at the top of the hill at an altitude of about 950 m. The pillars look like rock formations made of granite of various shapes, sometimes bizarre. They are all of different sizes within the range of 12-70 m. Some of the pillars form mini-groups and bear separate names, for example, Walls. Crown, Bowl. Declared a natural monument of local importance.

Shantar Islands
Archipelago in the Sea of Okhotsk with a total area of 250 thousand hectares. In 1999 they became part of the sanctuary of the same name, and in 2013 - a national park. The tourist season is in the summer months and September. There are many destinations, including whale watching, which is rare in Russia. Despite the abundance of leisure options, there are few visitors: this is due to the difficulties of travel and the high cost of excursions.

Petroglyphs of Sikachi-Alyan
These rock carvings were found in the Khabarovsk region. First described in the middle of the 19th century. They were made during the early Neolithic period. There are especially many rock formations and stones with petroglyphs along the right bank of the Amur, although they are also found in other places. Both scenes from the life of people and animals are drawn. Some drawings suggest what the fauna was like in antiquity.

Baikal-Amur Mainline
In short, BAM is one of the longest railway lines in the world, 3.8 thousand km. Opened in 1938, but construction took more than a decade. It connects the Irkutsk Region and the Khabarovsk Territory. At the moment, it needs expansion, as it operates at the limit of the bandwidth. The modernization project has already been launched.

Lotus lakes
They are located in different parts of the region. The most popular lakes: Tsvetochnoye, Velvetnoye, Lonchakovo. Just a few days in late July and early August, you can see Komarov's lotuses bloom. The water surface is covered with flowers, creating a unique natural canvas. Many legends and traditions are associated with this phenomenon. Supposedly, if you look at a lotus during the blooming period, you will be lucky all year.

Lake Amut
It is located in the Solnechny district at an altitude of 761 m above sea level. The water temperature does not warm up above +6 ° C. It is a landslide type, as it was formed due to the descent of mountain masses from the slope, as a result of which the channel of the river of the same name was blocked. On the shores there is light woodland, including low shrubs, the relief is heterogeneous, and the snow lies until mid-summer.

Khabarovsk bridge
Part of the Trans-Siberian Railway, laid through the Amur near the capital of the region. The total length (with overpasses) is almost 3.9 thousand km, the width is about 25 m. It was opened in 1916, but was repeatedly completed and reconstructed. It was especially strongly transformed in the late 90s of the last century, when the old spans were dismantled and modern ones began to be used. In Khabarovsk, tourists are received by a museum founded in honor of the bridge.

Bologna nature reserve
Created in the Middle Amur lowland in 1997 on an area of more than 100 thousand hectares. The name was given in honor of the lake bordering the reserve. The main task is to preserve and study bog complexes, which occupy up to 80% of the territory. In addition, an important factor is that the migration routes of some rare bird species pass through the reserve. We need to provide them with safe parking and not change their familiar environment.

Toki Island
Since 1987 it has been recognized as a natural monument of local importance. It is located in the Vininsky district and covers an area (together with the security zone) - about 1.2 thousand hectares. It has a zoological profile, since the island is a rookery of pinnipeds - Larga seals, sea lions, walruses. In 2007 it became a private reserve. Excursions are free, no one lives on an ongoing basis, so you need to make an agreement in advance.

Bolshekhekhtsirsky reserve
It has existed since 1963. Occupies an area of 45 thousand hectares. Named after the mountain range. Most of the territory is covered with forests. Despite the proximity to settlements, the reserve is rich in different types of fauna. There are even Himalayan bears and Amur tigers. The Museum of Nature receives tourists on an ongoing basis, eco-routes have also been developed, and the Aralia Visitor Center is operating.

Botchinsky reserve
Initially it had the status of a nature reserve, but in 1994 it became a nature reserve. The area is 267 thousand hectares. The relief is mountainous and inhomogeneous, the elevation changes are within 500 m. The Amur tigers come here, this is the northernmost point of their habitat. Found fossils of plants that are millions of years old. The reserve, within the framework of environmental education, cooperates with schools and participates in regional eco-projects.

Dzhugdzhur reserve
Created in 1994. Occupies 860 thousand hectares of Ayano-Maisky district. The largest nature reserve in the region. Since it is located on the coast, it also includes a part of the Sea of Okhotsk. The staff offer tourists two route schemes when visiting the reserve. You cannot deviate from them, and before entering the territory, you must obtain permission by signing under the code of conduct.

Komsomolsky reserve
It was formed in the central part of the region in 1963. The area with water area is 64 thousand hectares. Part of the territory is the Amur Valley, 80% is forests. Notable places: the Steller's sea eagle nesting site, the ethnographic museum, adits left over from the construction of the Talandinskaya hydroelectric power station. Three hiking and two water routes have been developed for tourists. They vary in length and take from 1 to 4 days.

Amur cliff in Khabarovsk
It can be found on the Nevelskoy embankment. It has been known since 1858, when a camp was set up here. The bloody story of the execution of musicians in 1918 is associated with this place. Gradually, a museum and cultural center of the same name was formed here. He occupied the building of the former rescue station. Inside, the classic interiors of different times, typical for Khabarovsk, have been recreated.

Grado-Khabarovsk Cathedral
Another name is "In the name of the Assumption of the Mother of God." Built in the 80s of the XIX century. Became the first stone temple in the city. With him there was a bell tower and two lateral limits. In 1930, the cathedral was dismantled.In the 90s, a new project was developed and a reconstructed building was erected on the same site. The appearance is significantly different, but some details are intentionally retained. Shrines are ancient icons.

Admiral Nevelskoy embankment
Located in the historical part of Khabarovsk. Named after the admiral, leader of two research expeditions. In the center - "Amur Cliff" with an observation deck. The embankment is a place for walking and holding all kinds of city events. From here, in good and clear weather, China is visible. Free Wi-Fi is available in the area. The monument to Muravyov-Amursky, the pier and the beach are very close.

Khabarovsk city ponds
Are of artificial origin. There were ravines at this place until 1983. The area around is ennobled, something like a small park is laid out. There are only 3 ponds: Lower with a fountain and lighting, Middle, where you can ride on special boats, Upper, in addition to light and fountains, it surprises with concerts of classical music. There are many sculptures on the territory, there are benches, cafes, play areas.

Transfiguration Cathedral
Built in the early 2000s in Khabarovsk with the blessing of Patriarch Alexy II. After lighting it became a cathedral. It has two limits, the small one is under the main one. The inner walls are painted with frescoes. The five golden domes appeared thanks to donations from parishioners and community organizations. The height of the building is 83 meters, which makes the cathedral one of the tallest in Russia.

Temple of Seraphim of Sarov
Construction began in Khabarovsk in 2003, and the temple was illuminated in 2008. The white-stone building was built according to the original project and has no analogues. It looks more like a merchant's chambers, crowned with a dome, and not like a cloister. The main shrines are a particle of the relics of Seraphim of Sarov and his icon. On the site of the wasteland surrounding the temple, a landscape park has now become a picturesque resting place for the townspeople.

Far Eastern Art Museum
Located in Khabarovsk since 1931. The largest collection of fine art objects in the region. Most of the collection came from the funds of the Hermitage, the Tretyakov Gallery and other museums in the country. Over time, icons were added to the painting. The exhibition activities of the museum are extensive, including other regions and abroad. He also regularly hosts exhibitions of similar subjects.

Khabarovsk Regional Museum named after Grodekov
Founded in 1894. It bears the name of the Governor-General. The exposition is divided into thematic parts: geology, flora and fauna, indigenous peoples, development of territories and others. On an ongoing basis, it accepts temporary exhibitions of different directions. The building was built specifically for the museum and is an architectural monument. New halls were added to it twice. In a more modern one, the skeleton of a whale is displayed.

Expocentre KnAAPO
It has been operating in its current form since 1999. Prior to that, in Komsomolsk-on-Amur there was a museum at an aircraft plant. When the exposition became part of the expocentre, the number of areas of exhibition activity increased. The area of the premises is 1.3 thousand square meters. The exhibitions tell the story of the enterprise and the domestic aviation. Employees hold meetings with current and former employees, give lectures.

Monument to Muravyov-Amursky
The statue of the Governor-General appeared in Khabarovsk in 1891. The opening was attended by Nicholas II, who had not yet set foot on the throne. The monument is guarded by a guard, which is located in a nearby house. The pedestal under the sculpture has several tiers of different height and shape. Muravyov-Amursky himself is depicted in full growth. The composition has five commemorative plaques with inscriptions and historical references.

Monument to Erofei Khabarov
Installed in 1958 in Khabarovsk in front of the railway station. Dedicated to the explorer, after whom the city is named. There is no portrait resemblance to the prototype, the author's fantasy reflected the general features and symbolism of this figure for the edge. In 2008, reconstruction was carried out, a plaque with the name of the sculptor Milchin was installed, and the monument itself received an official name.

Amur Botanical Garden
The only one in the region, has been operating since 1988. The collection is collected from local and exotic plants growing around the globe. In total, there are about 600 specimens in the garden. Nearby, thanks to the created comfortable conditions, species characteristic of different climatic zones coexist. Tourists can purchase ornamental plants for the home, as well as take courses that teach how to take care of greenery.

National Park "Anyuisky"
It has been located in the Nanai region since 2007. Occupies an area of 429 thousand hectares on the right bank of the Amur. It also includes a part of the Sikhote-Alin mountains. Since it is difficult to get there, this natural cluster has remained intact and has not been influenced by humans. The territory is dominated by deciduous forests and Korean cedar. There is only one settlement within the park.

Zoo "Priamursky"
Located near the capital of the region. Has been working since 2002. In this zoo, every pet is a native of the Far East. They were placed in spacious open-air cages that closely resembled the natural habitat of animals. All individuals were on the verge of death and could not survive in their natural environment, so they came under the supervision of the zoo staff. Among the inhabitants there are red deer, leopard, polar bear.

Sisiman Stone Forest
The natural monument is located in the Vininsky district in the bay of the same name. Received its current status in 1992. The phenomenon itself has been known since the 18th century. Occupies an area of 20 hectares. Branches and trunks of trees in the distant past were sealed with hot lava. Now you can see their manifestations on the coast. When the "protective" crust disappears due to environmental influences, the structure of the trees becomes visible.

Amur river
The length is 2.8 thousand km. On the territory of Russia, it flows through several regions, and also belongs to the Chinese lands. The estuary is the Sea of Okhotsk. It is navigable and of great importance, both in the economic activity of the country and in tourism. It is rich in fish, along the coast there are many natural and historical attractions. Over the past decades, it has often spilled heavily, causing floods.